RFID tags and labelsare the basic elements of remote radio identification systems. They record identification data that can be read remotely using radio waves from a distance of up to several hundred meters.
The RFID tag is placed in a label that looks like a traditional one with a 1D or 2D code. It is also prepared similarly.
The RFID printer prints information on the paper part and at the same time encodes the identification data in a hidden tag.
Labels prepared in this way are placed on containers, pallets, collective packaging and even individual products.
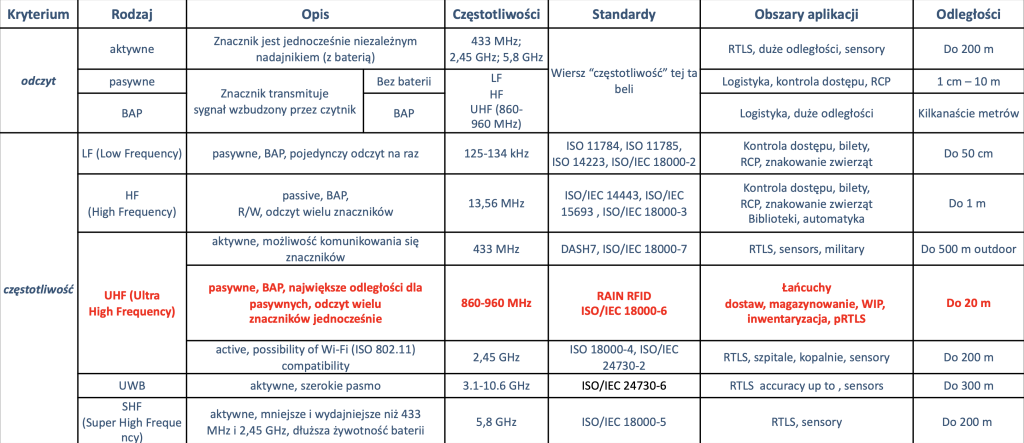
Depending on the method of powering RFID tags, the following are distinguished:
The RFID tag inlay consists of 2 elements:
Most UHF tags comply with the Class 1 Generation 2 (ISO 18000-6C) standard and use a minimum of 96 bits of memory to store EPC (Electronic Product Code). Some tags are more expensive because they have expanded user memory to store more information (usually 512 bits).
| Parameters | RFID | Barcodes |
| Reuse | tags can be read and written again | no possibility to change data, static information |
| Lifespan | over 10 years | depends on the medium on which the code is placed |
| Use in difficult environmental conditions | possibility of using markers in difficult conditions, e.g. atmospheric, temperature | low strength, depending on the material on which it is placed |
| Possibility of reading in case of damage | none | exists depending on the degree of damage |
| Effect of interference caused by magnetic field | may affect tag reading efficiency | no impact |
| Scope of stored data | even over 128 kB | depending on the type. symbolism used, min. 8 characters |
| Costs | depending on the characteristics of the tag, min. approx. USD 0.08 per tag | low production cost approx. USD 0.01 |
| Applying to an object | identification requires at least two steps: producing the tag and placing it on the object | single step: e.g. printing directly on the packaging |
| Visibility of marking | not required | required |
| Reading distance | up to 100 m (in optimal conditions) | up to 4 m (using standardized materials) |
| Traceability | unique (series) at the level of piece, collective packaging, pallet | identification at the level of a specific category |
| Reader orientation | any | aligned to code direction orientation (using a single laser beam) |
| Simultaneous identification | several hundred tags per second (with anti-collision mechanism applied) | reading single codes |
| Security, anti-theft systems | very high level of security, practically impossible to clone | easy to forge, copy |
| Data confidentiality | if the tag has not been destroyed or deactivated, it can be read remotely, e.g. on a product that has left the store | no data available for remote reading |